In the intricate world of payment processing, acquirers play a crucial role in facilitating seamless transactions between merchants and customers. If you’re a business owner or an individual eager to grasp the fundamentals of payment processing, understanding what an acquirer is and their responsibilities is essential. In this comprehensive guide, we will explore the role of acquirers in the payments ecosystem, their key responsibilities, and how they differ from other entities in the financial realm.
What is a Bank Acquirer?
At its core, an acquirer is a financial institution, typically a bank, that partners with merchants to process payment card transactions. When a customer makes a purchase using a debit or credit card, the acquirer works as an intermediary, facilitating the transfer of funds from the customer’s bank to the merchant’s account.
Key Responsibilities of an Acquiring Bank
The role of an acquiring bank involves several critical responsibilities, including:
- Transaction Authorization: Acquirers verify the validity of payment card details and approve or decline transactions based on available funds and security checks.
- Settlement: Acquirers handle the settlement process, ensuring that funds from approved transactions are transferred from the cardholder’s bank to the merchant’s account.
- Risk Management: Acquirers assess and manage the potential risks associated with processing transactions, including fraud detection and prevention.
- Compliance: Acquiring banks must comply with various industry regulations and security standards to ensure the safety and integrity of payment card data.
Understanding Acquiring Bank Fees and Services
Acquirers offer a range of services to merchants, including payment processing solutions, reporting and analytics, and customer support. They generate revenue by charging fees for their services, which may include interchange fees, processing fees, and chargeback fees.
Examples of Acquiring Banks
Popular examples of acquiring banks include well-known financial institutions such as XYZ Bank, ABC Merchant Services, and DEF Payment Solutions.
Who Needs an Acquirer and Why?
Any business that wants to accept credit or debit card payments requires the services of an acquirer. By partnering with an acquirer, merchants can expand their customer base and offer convenient payment options, leading to increased sales and customer satisfaction.
Acquirer’s Role in Transactions
When a customer makes a purchase using a card, the transaction involves multiple parties:
- Cardholder: The individual making the purchase with a payment card.
- Merchant: The business selling goods or services.
- Acquirer: The financial institution partnering with the merchant to process the transaction.
- Issuer: The bank or financial institution that issued the payment card to the cardholder.
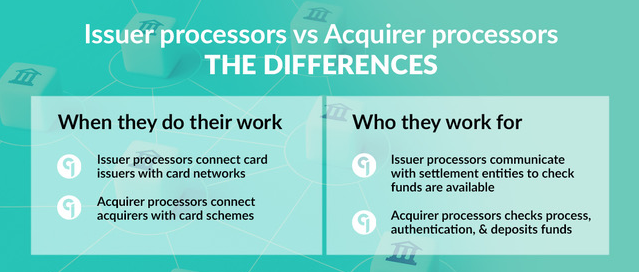
Acquiring Bank vs Issuing Bank
The key difference between an acquiring bank and an issuing bank lies in their roles within a payment transaction. While an acquiring bank works with merchants to process transactions, an issuing bank is responsible for providing payment cards to consumers.
Merchant Acquirer vs Payment Processor
Although the terms are often used interchangeably, there is a distinction between a merchant acquirer and a payment processor. A merchant acquirer, as discussed earlier, is a financial institution that partners with merchants to process card payments. On the other hand, a payment processor is a company or entity that provides the technology and infrastructure to facilitate the actual processing of the transactions.
FAQs about What Is an Acquirer
Q1: What is an acquirer reference number?
An acquirer reference number is a unique identifier assigned to each transaction processed by the acquiring bank. It serves as a reference for tracking and reconciling transactions in case of any disputes or inquiries.
Q2: Why do merchants need acquirers?
Merchants need acquirers to enable them to accept card payments from customers. Acquirers provide the necessary infrastructure, security measures, and expertise to process these transactions efficiently and securely.
Q3: What is the difference between an issuer and an acquirer?
An issuer is the bank or financial institution that issues payment cards to consumers. They provide the cardholder with access to a line of credit or funds. On the other hand, an acquirer is the financial institution that partners with merchants to process transactions and facilitate the transfer of funds from the cardholder’s account to the merchant’s account.